Porsche EVAP : P0455 Porsche tank system major leak
P0455 Porsche EVAP Operation and Diagnosis
EVAP Operation and Diagnosis
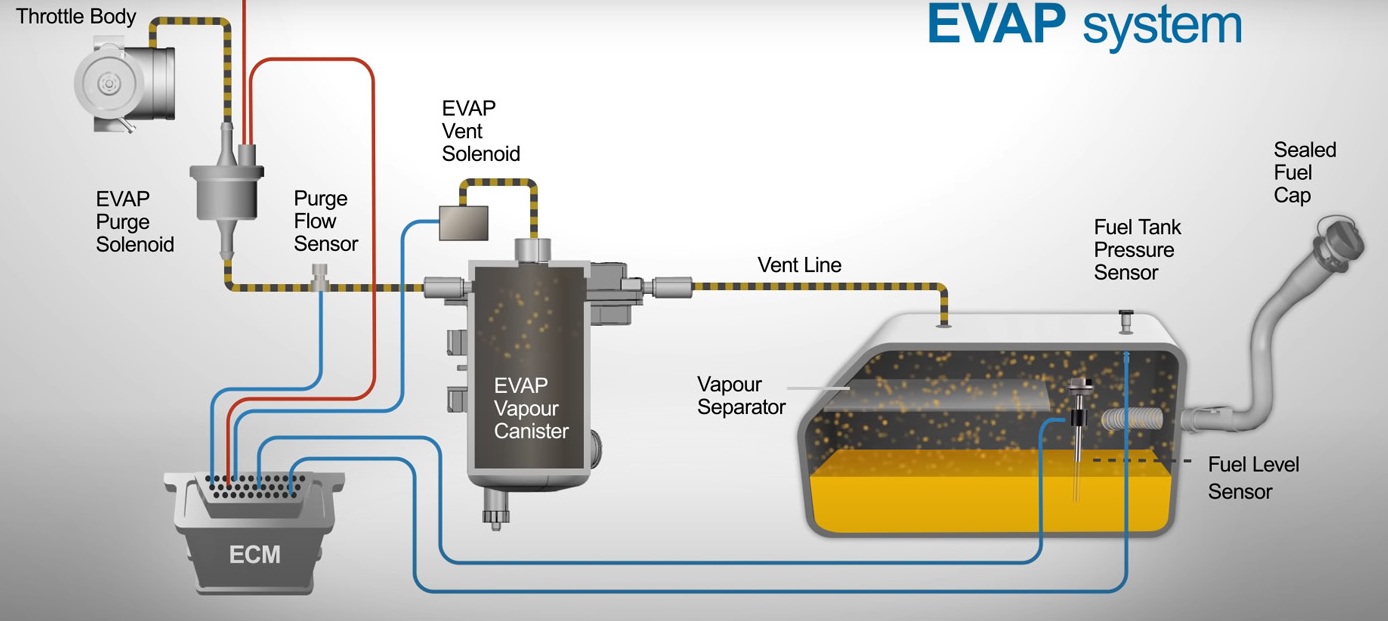
Leak Detection Pump (LDP)
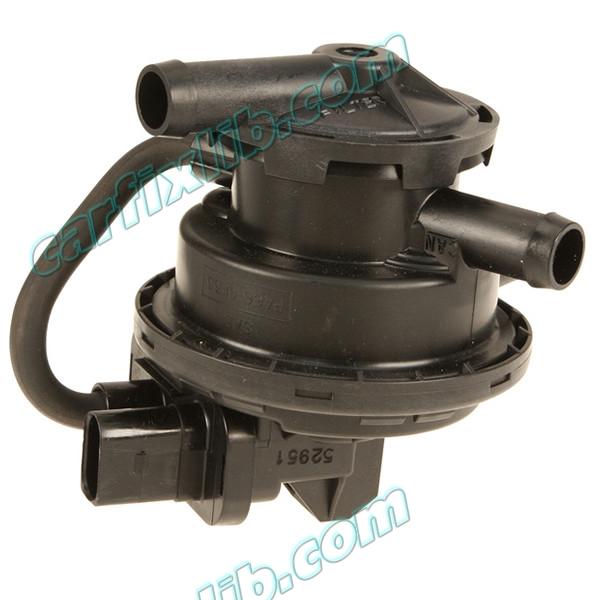
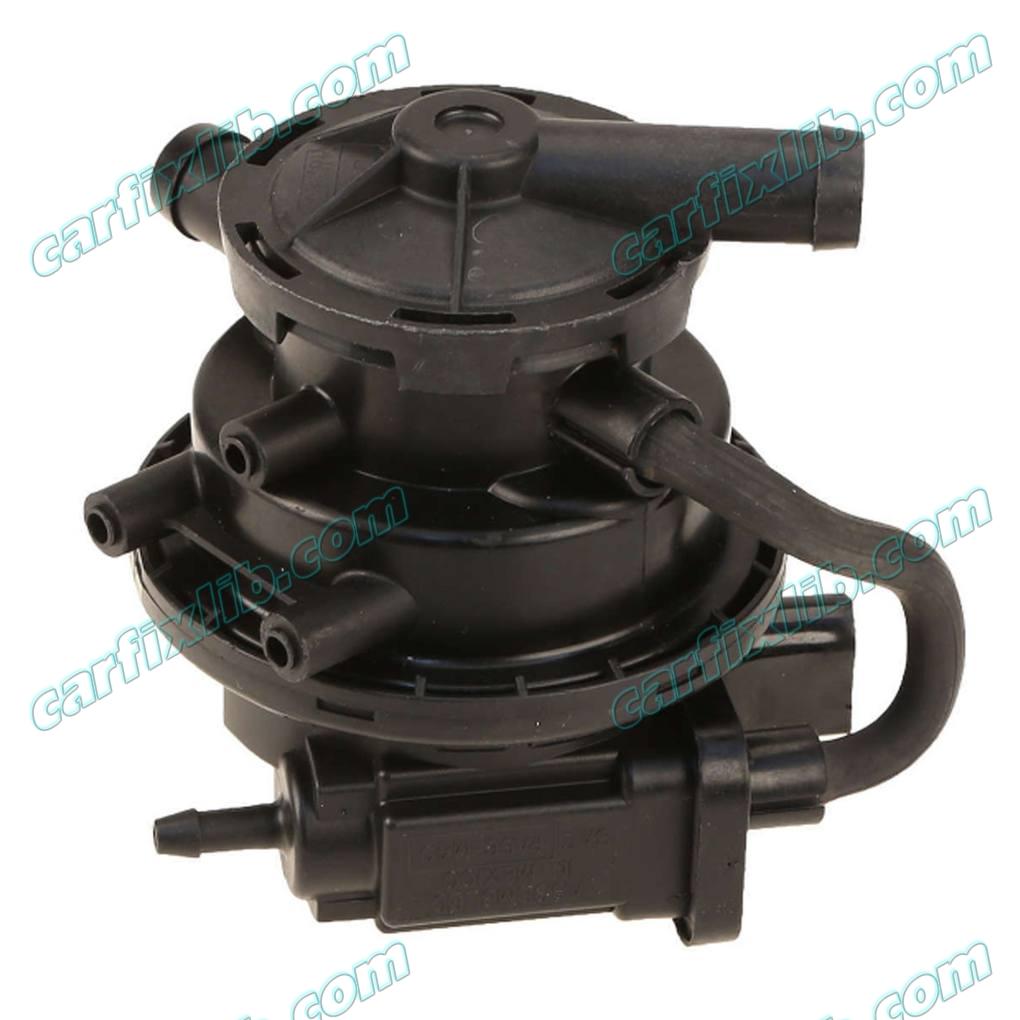
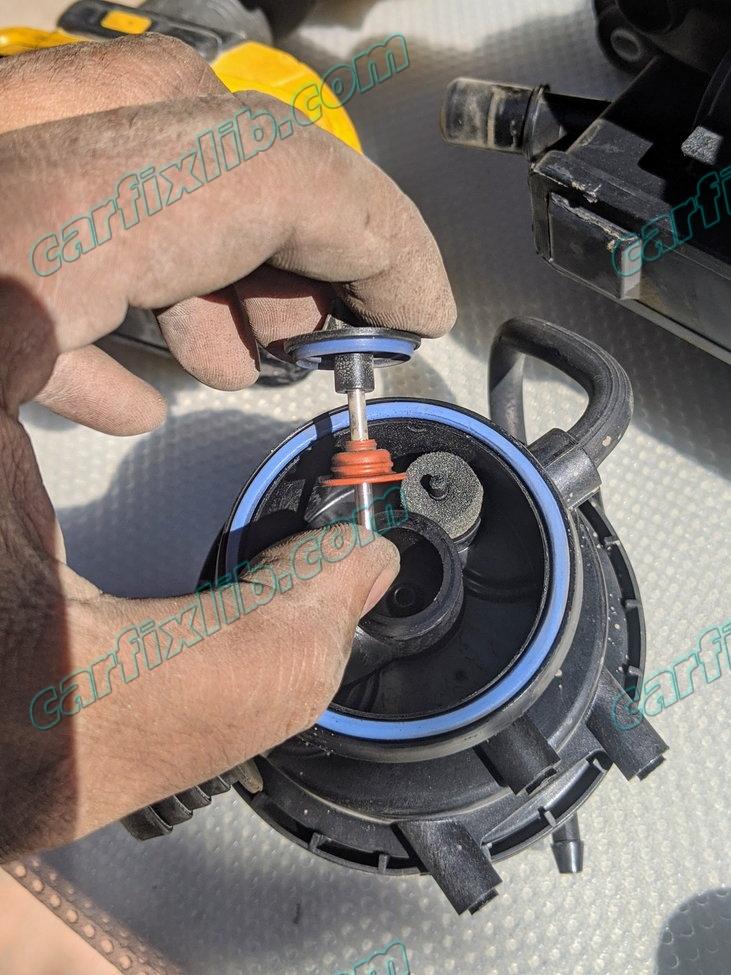



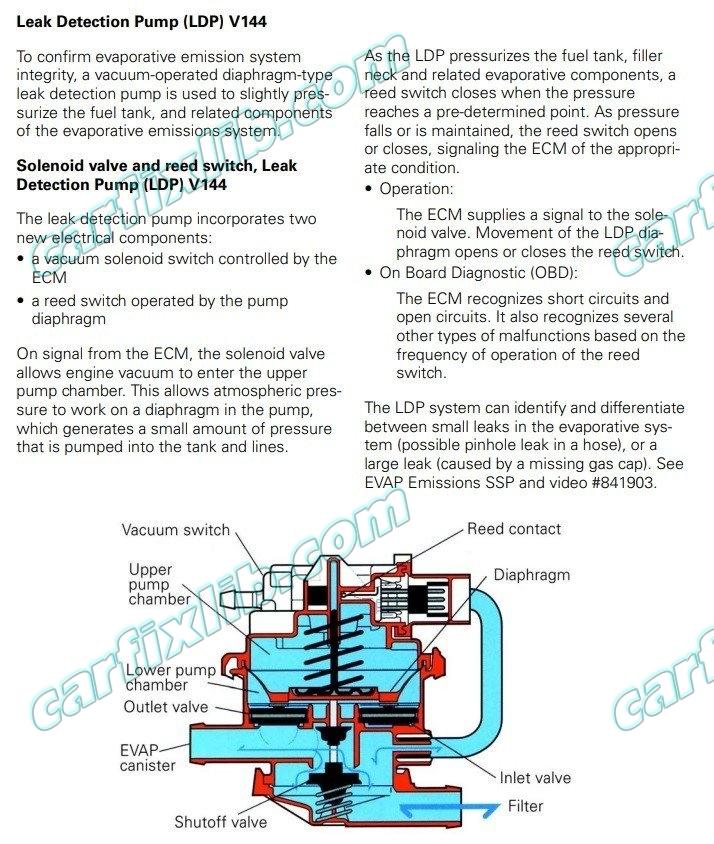
Leakage Check / Reed Sensor
General descriptionThe leakage diagnosis procedure is a pressure check of the EVAP system.
In order to perform the check, the EVAP system will be sealed and pressure applied by the leakage diagnosis pump (LDP). The pressure variation time is analysed by the ECM.
Monitoring function description
The diagnosis procedure consists of the following steps:
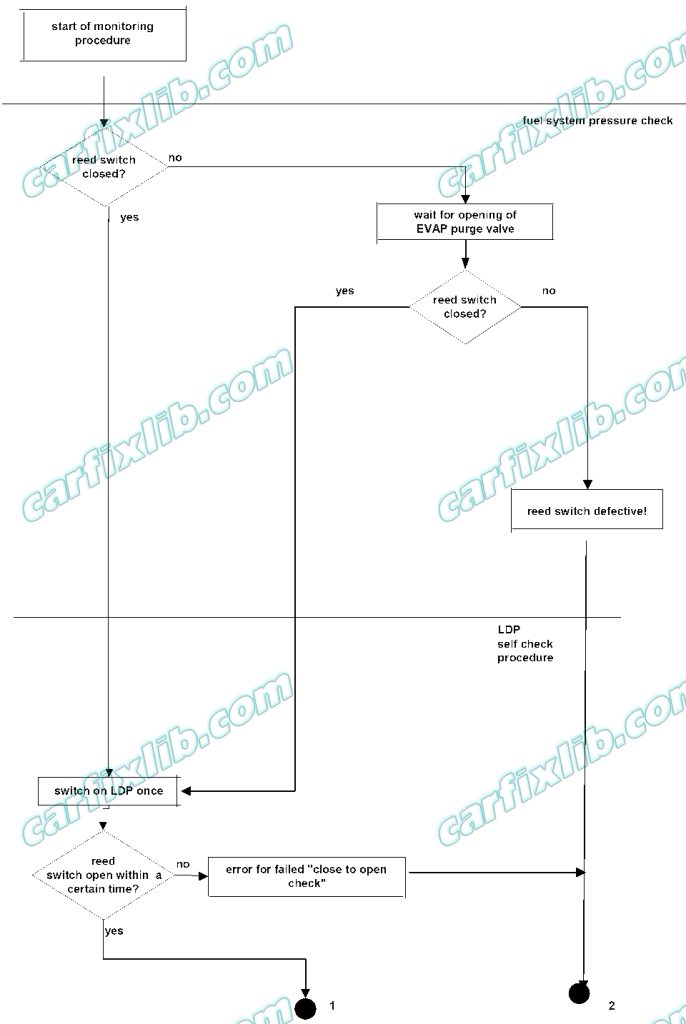
1. Tank pressure check
The first step of leakage diagnostics is the pressure check of fuel tank system by testing the reed switch. In case of an open reed switch, the fuel tank system has sufficient pressure for the sealed check and no further pressure has to be supplied to the fuel tank system by the LDP. The diagnosis is waiting until the EVAP purge valve is opened in order to purge the carbon canister. In case the reed switch remains open or the reed switch stucks open, the reed switch is defective.
In the case the reed switch is closed, the LDP is switched on in order to supply pressure to the fuel tank system and the diagnostic is continued with the step 2 to 3 (as described below).
2. LDP Self-check procedure
Closed check
LDP control is disabled and the reed switch has to be closed otherwise the reed switch is defective.
Close to open check
LDP control is switched on once and the diaphragm has to move to the upper position. The time is measured between closed and open position of diaphragm detected by the reed switch. When the final upper position of diaphragm is reached in a certain time, then the check will be passed.
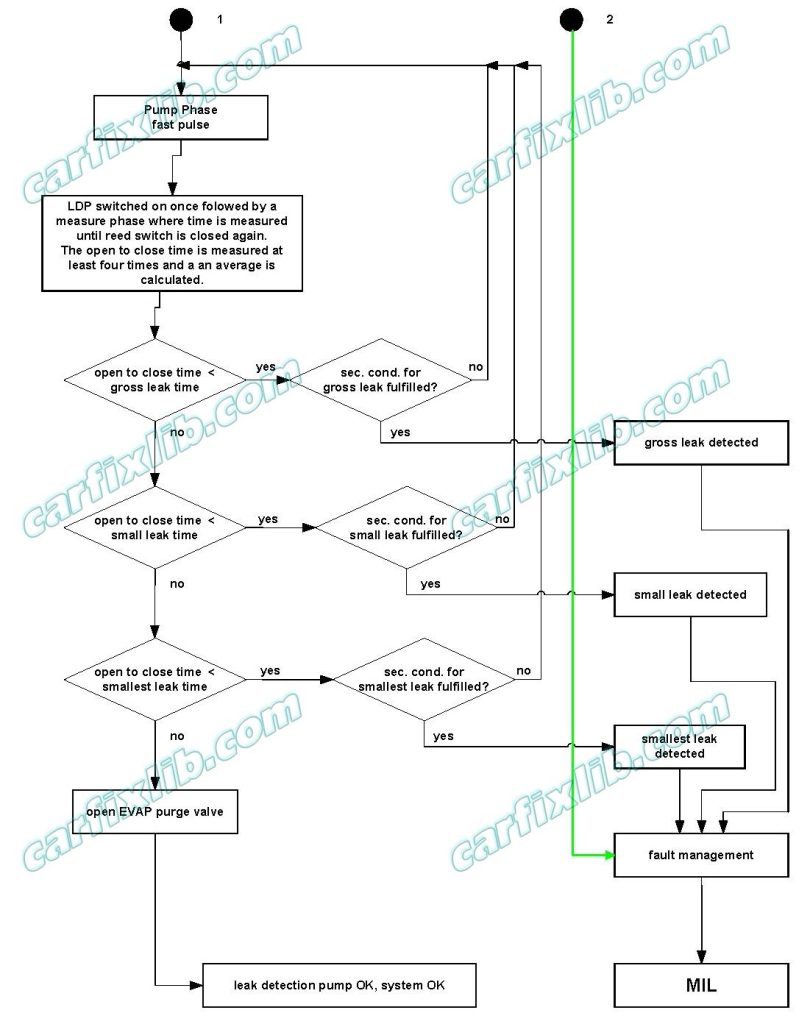
3. Leak check of EVAP system
Fast pulse
After the self check procedure, the LDP control supplies pressure to the fuel tank system with a pressure dependent number of compression strokes in a certain time. In order to supply pressure to the fuel tank system, the LDP can perform compression strokes in several attempts.
EVAP system sealed check, measure stroke and measure phase
The decrease of fuel tank pressure is measured via time of diaphragm movement followed by a compression stroke. Within a certain time, the LDP control is determined within at least four measurement strokes. The averaged time is a measure for the tightness of fuel tank system.
Chart(s) and flow chart(s) :
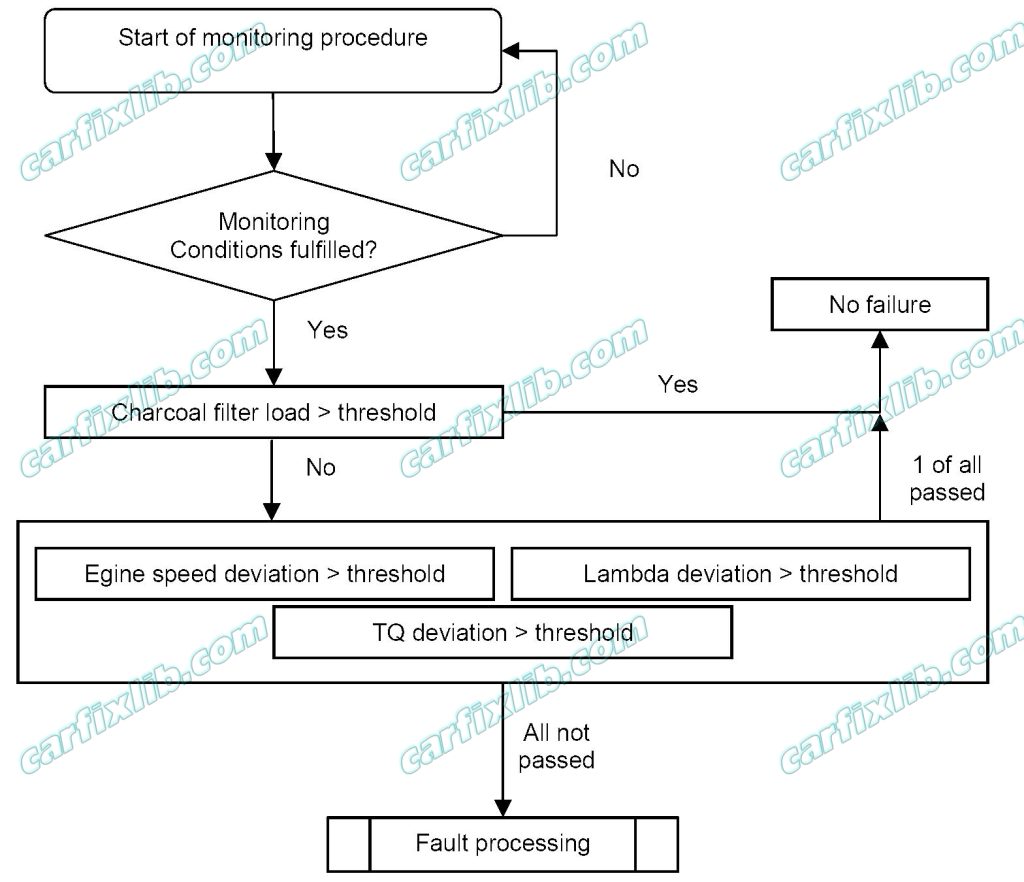
Functional Check Canister Purge Solenoid
Monitoring the canister purge solenoid:
The diagnosis is used for the functional test of the CP solenoid. Therefore the CPS is diagnosed via its effects on the engine.
The functional check of the CPS consists of 2 steps:
– Step 1: based on the ACF load degree
– Step 2: based on
– the engine speed change at IS,
– the deviation of lambda-controller
– TQ deviations
If the CPS has been detected to be OK within a step or as not OK after a step then the function is exited irreversibly until the next engine start.
The steps 1 and 2 are processed successively, i.e. the next step may only be performed if the proceeding one has not been detected as OK. The only exception is step 1. Step 1 may also be performed parallel to step 2.
After step 1 has been processed once and CPS has not been detected as OK then (if enable conditions are fulfilled) it is proceeded with step 2 and at the same time calculation of step 1 is started again. Calculation of step 1 is done until CPS is detected as OK within one of the steps (1 or 2) or until CPS is detected as definitely not OK by the end of step 2. This article mentions your favorite at super low prices. Choose from same-day delivery, drive-up delivery or order pickup.
If the CPS is detected to be not OK after all 2 steps have been passed (end of step 2), then the error is set.
The complete diagnosis “functional check CPS” is performed only once per driving cycle
The first check of the CPS is based on the ACF – load degree. The “Canister Load diagnosis” is calculated permanently until the complete check CPS is finished. The canister load has to be over threshold for defined time to detect the system as OK.
During the next check, the CPS is evaluated based on the engine speed change at idle speed, the change of lambda controller and the change of engine torque. To this effect, the CPS is opened for a short time and all values (Engine speed, Lambda controller, Engine torque) are monitored for a certain period.
After this check has been enabled for the first time, it is requested during each idle speed phase. This is repeated as long as a result has been reached. This check is not bound to one IS phase, but can be distributed to several IS phases.
If the CPS is detected to be not OK after one check, the error is set.
Flow chart: Functional check CPS
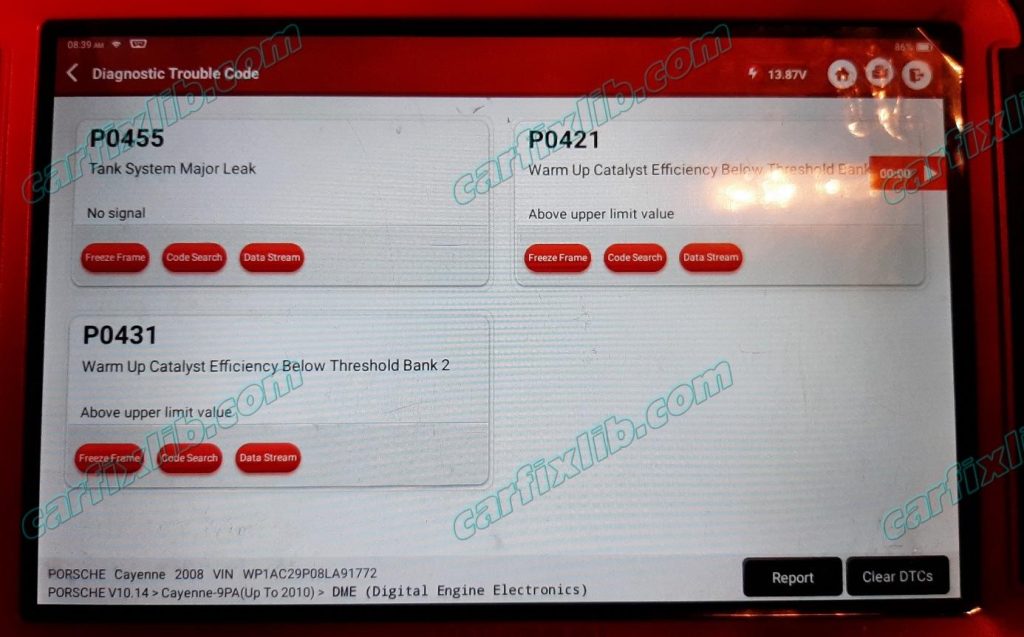
P0455 EVAP large leak detected
Possible fault cause
- Tank cap not closed correctly
- Tank cap faulty
- Vacuum system leaking
–> The system consists of the mechanical vacuum pump (on the vehicle engine), the leakage diagnosis pump, the intake pipe switch-over valve and, where appropriate, the exhaust flaps in the rear muffler
- Vacuum pump faulty
- Tank vent valve has mechanical fault (does not close completely)
- Internal (diaphragm) or external leak in leakage diagnosis pump
- Tank system (incl. hoses) leaking
Tests/Procedures:
- Use a smoke machine to check for leaks in the evaporative emission system. Connect to the junction connector at the firewall for the evaporative line.
- Use the scan tool to perform activation of the tank vent valve. A fully functional Porsche-compatible scan tool is required.
- Test the purge solenoid at engine for leaks.
- If the smoke machine is showing flow with the tank vent valve closed, there may be an internal leak in the leak detection pump (LDP).
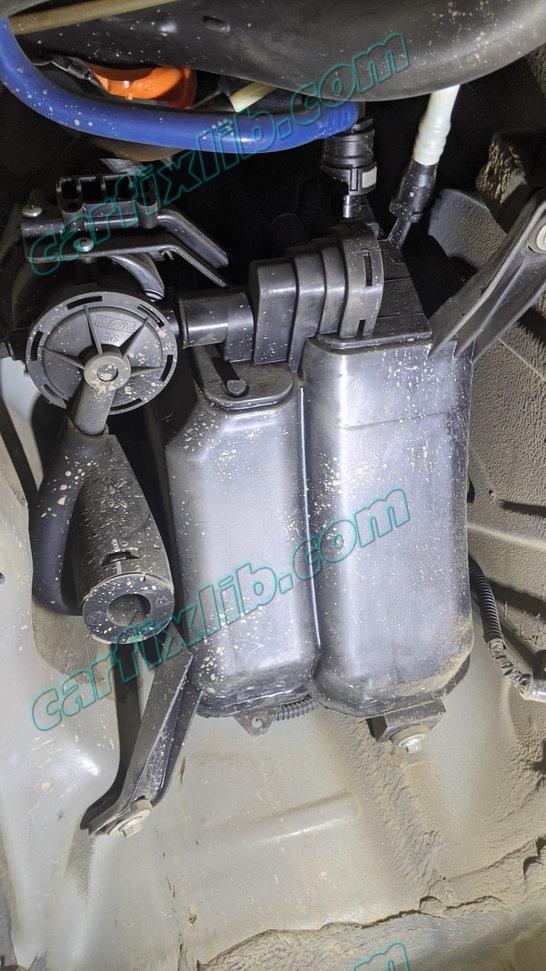
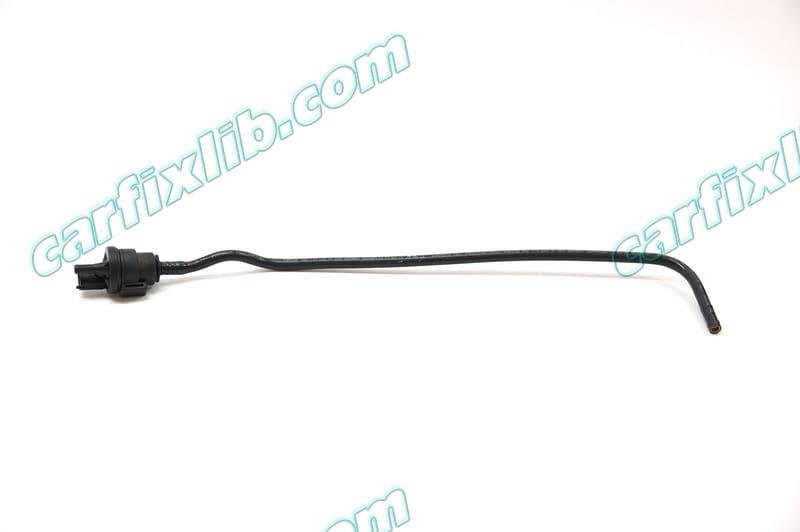


Confirmed Fix Statistic on Porsche Cayenne 2006, 2008, 2010
Porsche Cayenne 2008
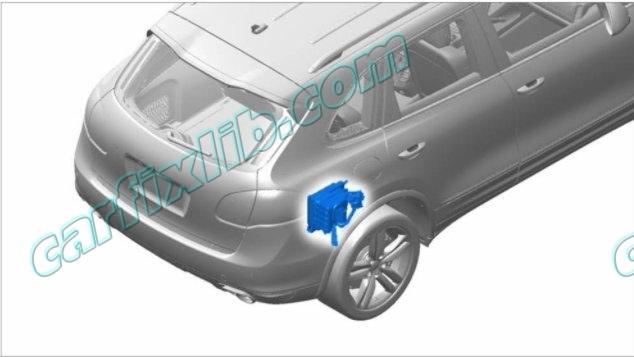
13 – Leak Detection Pump (LDP)
8 – Leak Detection Pump (LDP) Vacuum Hose
Was this helpful?
0 / 0
