BMW – HVAC Heating and air conditioning Flap Motor functions
Flap motors
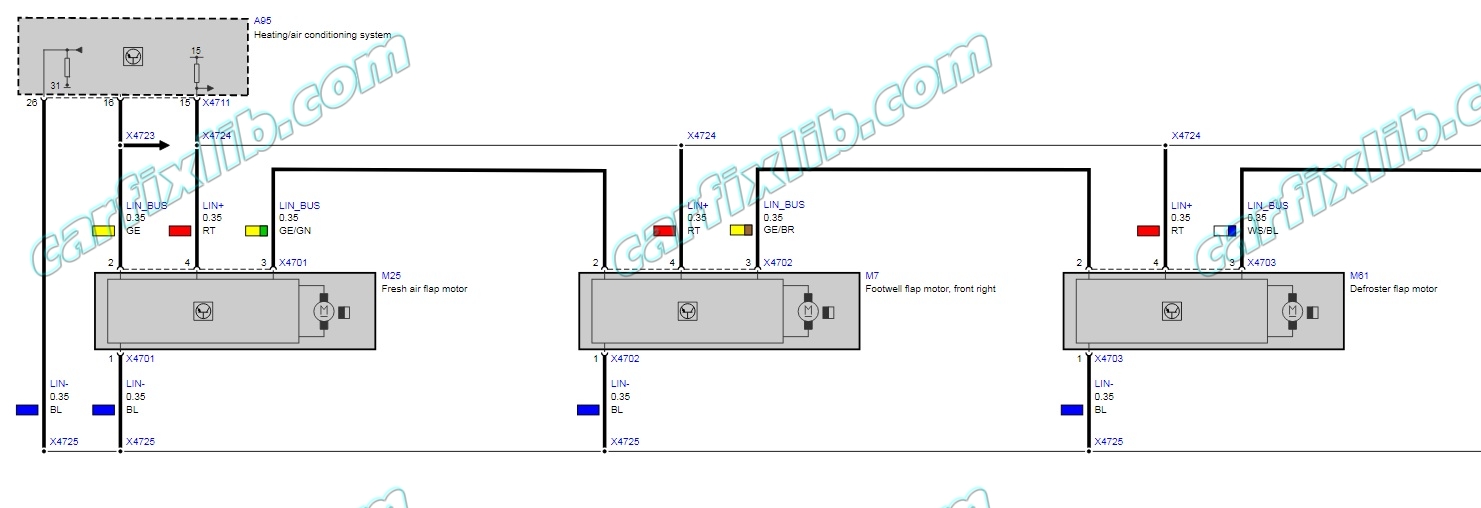
The flap motors are actuated by the IHKA control unit via the LIN bus and are supplied with power and an earth connection. In the rest state, the control unit switches the supply voltage off.
The flap motors communicate across the LIN bus with the IHKA control unit. The flap motors are switched in series on the LIN bus.
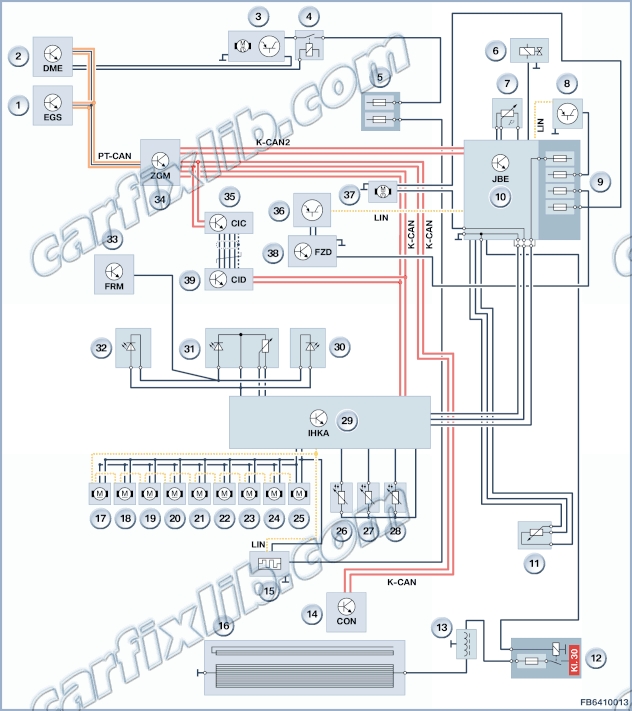
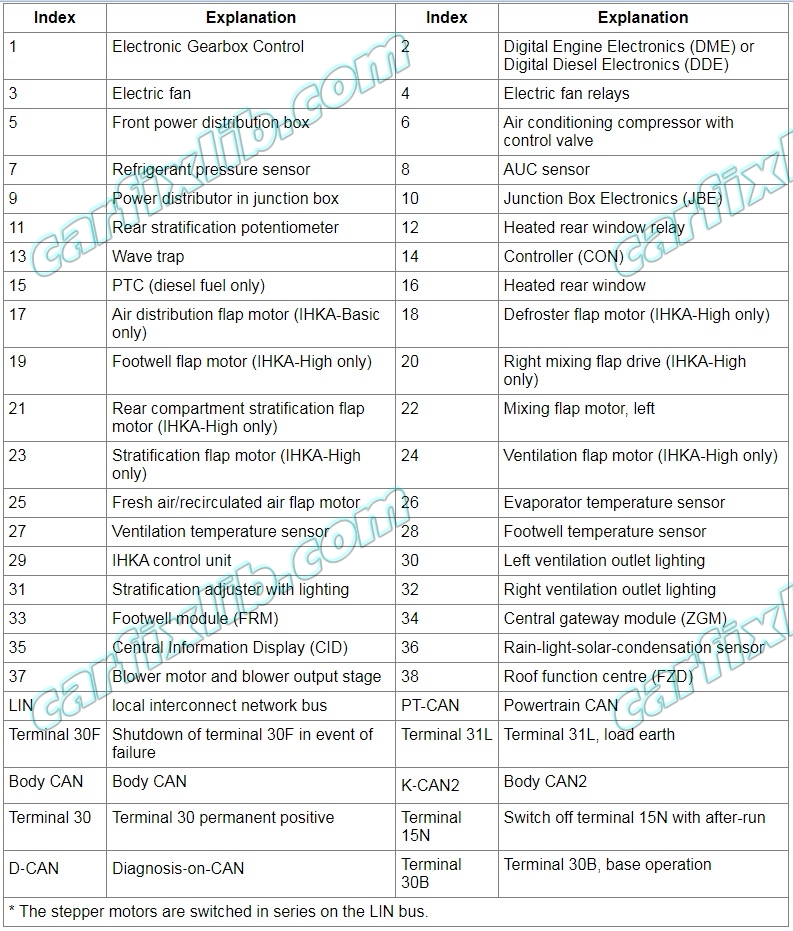
The flap motors in the integrated heating and air conditioning system (IHKA) are all identical. Differences in operation are due only to the respective programmed address. Each flap motor is assigned a certain address. The address determines which function the flap motor assumes in the system network. This address is how the rear compartment flap motor, for example, identifies messages that are addressed to it (e.g. open flap). This address is also how the IHKA control unit, for example, knows which flap motor has issued a fault message.
Prerequisite for successfully addressing the flap motors is correct encoding of the IHKA control unit.
After starting auto-addressing, the last flap motor in the series connection topology is programmed with its address. Then the penultimate flap motor in the topology is programmed with its address and so on until all the addresses have been assigned. Therefore the installation position of the flap motor in the wiring harness decides which address is programmed to the flap motor.
If, for example, the last flap motor in the topology is not connected to the IHKA control unit wiring harness during the auto-addressing process, or there is no connection through the local interconnect network bus: The penultimate flap motor in the topology is wrongly identified as the last flap motor in the topology. As a result this flap motor is assigned the wrong address. The remaining stepper motors also receive the wrong address. The wrong addresses are also assigned if the connectors are mixed up. This post is sponsored by our partners.
If several flap motors are entered in the fault memory with the fault ”not responding”, then there is probably an open circuit in the connection through the local interconnect network bus. The open circuit (wiring, connector, flap motor) should be looked for in the flap motor that comes first in the topology out of all the flap motors entered.
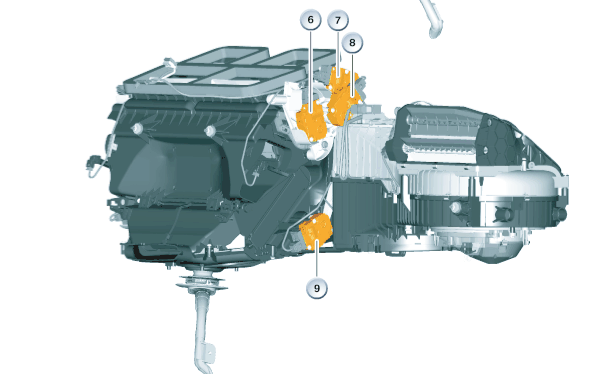
The following flap motors are installed in the high equipment heating and air conditioning system (IHKA):
- Fresh-air-flap motor
- Front right footwell flap motor
- Defroster flap motor
- Mixing flap drive, right
- Front right stratification-flap motor
- Front left footwell flap motor
- Front left stratification-flap motor
- Mixing flap drive, left
- Rear compartment flap motor
The list order is the same as the activation sequence via the local interconnect network bus. The flap motors are connected to the IHKA control unit by 4-pin plug connections.
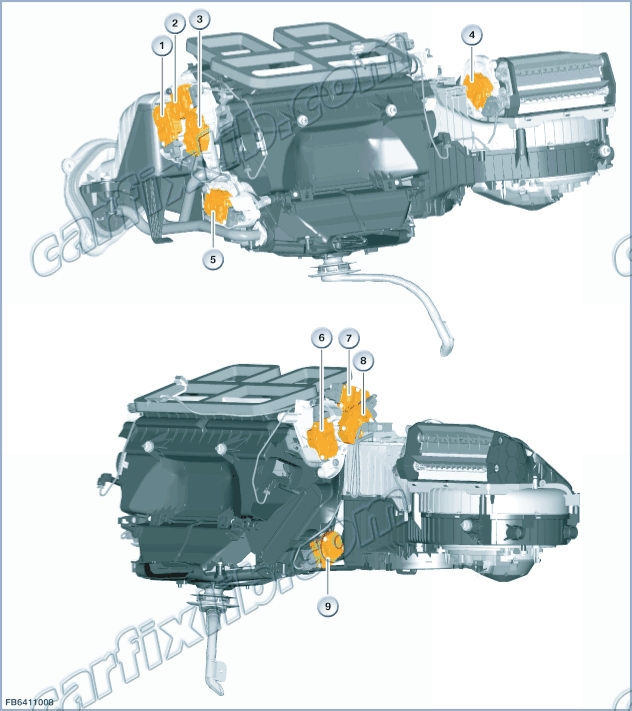
| Item | Explanation | Item | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Front left stratification-flap motor | 2 | Front left footwell flap motor |
| 3 | Front left mixing flap drive | 4 | Fresh-air-flap motor |
| 5 | Rear compartment flap motor | 6 | Mixing flap drive, right |
| 7 | Mixing flap drive | 8 | Front right footwell flap motor |
| 9 | Front right stratification-flap motor |
The following flap motors are installed for the basic version heating and air conditioning system (IHKR):
- Fresh-air-flap motor
- Mixing flap drive
- Air distribution flap motor
The air distribution flap motor has the task of setting the air distribution over a cam disc. The air distribution flap motor has no way of recognising the actual position. Despite this, two cams of different widths are provided on the cam disc to allow the cam disc to be unambiguously positioned. A microswitch signals to the control unit that the cams have passed over. This mechanism achieves reliable and rapid positioning of the cam disk.
Air distribution flaps, mixing air flaps, stratification flaps
The air distribution flap motors ensure that the air can be distributed specifically across the ventilation grilles in the vehicle. The mixing air flaps (if installed) regulate the air at the required temperature. The stratification flaps (if installed) also influence the blow-out temperature in the ventilation area.
It is therefore important that the air distribution, mixing air and stratification flaps and fully functioning and the ventilation grilles are open in order to heat the passenger compartment with the auxiliary heater.
The flap motors are powered by stepper motors.
Possible fault causes with the air distribution flaps
Symptom of faulty air distribution flaps
Faulty air distribution flap drives can prevent or severely restrict the air flowing into the passenger compartment. This causes little or no heating effect in the vehicle.
Faulty mixing air flap drives or stratification flap drives can prevent the air from being sufficiently heated (little or no heating effect in the vehicle).
Measures
A faulty flap drive is suspected, or a fault code entry relating to a flap motor is present, select and work through the ‘Check flap drives’ item from the main menu.
For information purposes
Obstructions detected within the stepper motor travel range indicate a mechanical problem near the air distribution flap.
No communication means:
- If only one stepper motor is affected, indicates an electrical fault with the stepper motor in question.
- If several stepper motors are affected, indicates a fault in the local interconnect network bus line or a connector problem before the first affected stepper motor in the wiring harness.
- If a stepper motor has the wrong address, the expected stepper motor (i.e. the correct stepper motor address) would not participate in communication on the local interconnect network bus. A communication fault is entered due to the missing response telegrams from the affected stepper motor address (does not answer). Auto-addressing the stepper motors may remedy this problem.
Was this helpful?
4 / 0
